In a world where precision and efficiency are paramount,the demand for advanced control systems has never been more critical. The rise of automation in industries ranging from manufacturing to robotics has propelled low-voltage direct current (DC) servo drivers into the spotlight. these compact marvels not only facilitate smooth and precise motion control but also promise significant energy savings, making them indispensable in modern applications.This article delves into the intricate workings of low-voltage DC servo drivers, exploring how thay blend technology and engineering to offer unparalleled performance. We will unravel the mechanisms behind their efficiency, examine their impact on operational costs, and highlight the role they play in revolutionizing today’s automated landscapes.Join us as we embark on a journey through the nuanced world of low-voltage DC servo drivers—where power meets precision.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Fundamentals of Low-Voltage DC Servo Drivers
- Evaluating Efficiency Metrics in Servo Driver Performance
- Enhancing Precision through Advanced Control Techniques
- Practical Recommendations for Optimal Servo Driver Integration
- Q&A
- In Conclusion
understanding the Fundamentals of Low-Voltage DC Servo drivers
Low-voltage DC servo drivers are essential components in the realm of motion control, enabling precise regulation of motor performance in various applications. These drivers convert low-voltage signals into proportional output, allowing for enhanced control over the speed and position of the motor. By utilizing feedback mechanisms,servo drivers can detect discrepancies in the motor’s movement and adjust in real time,leading to improved accuracy and reliability in operations.
One of the critical aspects of low-voltage DC servo drivers is their efficiency. These systems often leverage advanced control algorithms, allowing for optimal use of energy while minimizing heat generation.This efficiency results in several benefits:
- Reduced power consumption – Less energy wasted translates to cost savings.
- Extended service life - Lower operational temperatures contribute to longer longevity of components.
- Higher torque output – efficient systems can deliver greater performance in demanding applications.
The precision offered by these drivers is equally noteworthy. They are designed to operate within tight tolerances, making them ideal for applications that require high accuracy, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and medical devices. A breakdown of their performance characteristics can be illustrated as follows:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Repeatability | Achieves consistent results within 0.01 mm accuracy. |
| Response Time | Fast reaction to input changes, typically under 10 ms. |
| Control Range | Capable of handling a wide range of speeds and loads. |
Evaluating Efficiency Metrics in Servo driver Performance
When assessing servo driver performance, efficiency metrics serve as a beacon, illuminating the efficacy with which these systems convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. key metrics to consider include:
- Energy Efficiency: The ratio of output mechanical power to input electrical power.
- Thermal Performance: Heat generation as a byproduct of operation, impacting both longevity and reliability.
- Current Draw: The impact of load on the current required for optimal operation.
These metrics not only define performance but also influence overall system longevity and operational costs, making them critical for engineers and designers alike.
Another pivotal aspect of efficiency evaluation is the dynamic response of servo drivers under various loads. An optimal driver should not only exhibit high efficiency during steady-state conditions but should also maintain performance during transient conditions. Elements to consider include:
- Settling Time: The time taken for the system to reach a stable output after a disturbance.
- Overshoot: The amount by which the output exceeds its target value during a dynamic change.
- Steady-State Error: The difference between the desired and actual output once the system stabilizes.
Each of these parameters provides insight into the driver’s capability to maintain precision and adapt to changing operational demands.
Moreover, a comprehensive analysis of efficiency metrics frequently enough employs tables to present comparative data clearly. As a notable example, consider the following table summarizing performance metrics of different servo driver models:
| Model | Energy Efficiency (%) | Settling Time (ms) | Current Draw (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Servo driver A | 90 | 50 | 1.5 |
| Servo Driver B | 85 | 45 | 1.2 |
| Servo Driver C | 92 | 60 | 1.8 |
This format allows for a succinct comparison of various servo drivers, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses inherent in each model. Evaluating these efficiency metrics provides engineers with valuable insights into selecting the most suitable servo driver for their specific applications.
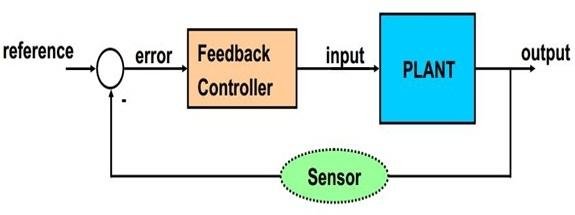
Enhancing Precision through Advanced Control Techniques
In the realm of automation and motion control, the quest for improved precision is paramount. Advanced control techniques have emerged as indispensable tools for engineers and developers striving to achieve impeccable accuracy in their applications. With the integration of algorithms like PID control, feedforward control, and adaptive control, low-voltage DC servo drivers can manage and respond to disturbances more effectively than ever before. These techniques allow for real-time adjustments, enhancing the system’s response and ensuring that the desired position and velocity are met with minimal deviation.
Furthermore, the implementation of digital signal processing (DSP) has revolutionized how servo systems operate. By utilizing DSP technologies, these drivers can process vast amounts of data at lightning speeds, making split-second adjustments to motor commands. This capability not only streamlines operations but also contributes to a notable reduction in errors. The advantages include:
- Enhanced tracking accuracy through elegant algorithms
- Noise reduction via advanced filtering techniques
- Improved system stability despite variable loads or external disturbances
As industries continue to seek out new approaches to boost efficiency, the role of feedback loops within these advanced systems cannot be understated. A well-designed feedback loop, integrating both position and velocity sensors, ensures that any displacement is promptly corrected. This dynamic interplay of signals translates to greater reliability and operational safety. The table below highlights key features of effective feedback systems in low-voltage DC servo drivers:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-resolution encoders | Precise positional feedback |
| real-time monitoring | Immediate correction capabilities |
| integrated diagnostics | Proactive issue detection |
practical Recommendations for Optimal Servo Driver Integration
When integrating low-voltage DC servo drivers into your systems, a few practical recommendations can significantly enhance performance. First, ensure that the power supply matches the servo driver specifications; this not only maximizes efficiency but also prolongs the lifespan of both the driver and the motor. Additionally, consider shielding and grounding techniques to minimize electrical noise, which can disrupt the precision of the servo driver’s response.
The configuration of the control signals is another crucial aspect. Utilize PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals for speed control to achieve smooth and accurate motor responses. It’s also advisable to implement feedback mechanisms that provide real-time data on motor position and speed, enabling closed-loop control. This approach enhances accuracy and helps identify potential issues early in the operation.
Lastly, regular maintenance and testing are vital to ensure optimal performance of the integrated system. Create a schedule for checking the condition of wiring,connectors,and other physical components. Employ diagnostic tools to monitor the performance and health of the servo drivers continually. Below is a simplified overview of common maintenance tasks:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect Wiring | Monthly | Prevent wear and short circuits |
| Test Feedback Systems | Quarterly | Ensure accurate performance |
| Check Power Supply Voltage | Monthly | Maintain optimal efficiency |
| Software Updates | As Needed | Enhance system capabilities |
Q&A
Q&A: Exploring Low-Voltage DC Servo Drivers: Efficiency & Precision
Q1: What are low-voltage DC servo drivers, and why are they vital in modern applications?
A1: Low-voltage DC servo drivers are electronic devices used to control the motion of servo motors at low voltage levels, typically under 60 volts. They play a crucial role in applications requiring precision and efficiency, such as robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems. their meaning lies in their ability to provide accurate motion control while minimizing power consumption and heat generation, which is essential for enhancing system longevity and performance.
Q2: How do low-voltage DC servo drivers enhance efficiency in systems?
A2: Efficiency in low-voltage DC servo drivers is achieved through several mechanisms. Firstly, their design often incorporates advanced algorithms for optimal control, reducing wasted energy during operation. Additionally, these drivers can quickly adapt to changes in load, ensuring that power is only used as needed. The result is not only lower energy costs but also improved battery life in portable applications,making them ideal for energy-sensitive operations.
Q3: What factors contribute to the precision of low-voltage DC servo drivers?
A3: The precision of low-voltage DC servo drivers stems from several key technologies. Feedback systems, typically involving encoders or resolvers, provide real-time data on motor position and speed. This information allows the driver to adjust power delivery instantly,leading to smooth and accurate motion. moreover, sophisticated control algorithms, such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control, enhance stability and responsiveness, ensuring that even the most delicate tasks can be performed with pinpoint accuracy.
Q4: Can you give examples of industries where low-voltage DC servo drivers are notably beneficial?
A4: Absolutely! Low-voltage DC servo drivers are widely used in various industries. In robotics, they enable precise movement for robotic arms and automated assembly lines. In medical devices, these drivers ensure accurate and reliable operations in surgical tools and diagnostic machinery. Additionally, they find applications in aerospace for control surfaces and in consumer electronics for camera stabilization and automated systems. Their versatility makes them a preferred choice across multiple sectors.
Q5: What are some challenges faced in the implementation of low-voltage DC servo drivers?
A5: While low-voltage DC servo drivers offer numerous advantages, some challenges exist in their implementation. One primary concern is the complexity of integration with existing systems,which may require considerable time and expertise.Additionally, managing electromagnetic interference (EMI) in densely packed environments can be difficult. Furthermore, ensuring compatibility with other components, such as sensors and controllers, can complicate designs. Nonetheless, careful planning and testing can mitigate these challenges effectively.
Q6: What future developments can we expect in low-voltage DC servo drivers?
A6: The future of low-voltage DC servo drivers is promising, with expected advancements in several areas. We may see increased integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for smarter control algorithms, further enhancing efficiency and precision. Advances in materials science could lead to lighter and more compact designs. Lastly, as the demand for automation and robotics grows across industries, we can anticipate innovations that will improve functionality, adaptability, and overall performance in low-voltage applications.
—
Q7: How can newcomers to this technology start exploring low-voltage DC servo drivers?
A7: For newcomers, starting with low-voltage DC servo drivers can be both exciting and accessible. Begin by studying the fundamentals of motion control and the roles of servos. Online tutorials, manufacturer datasheets, and forums are excellent resources. Additionally, consider engaging in hands-on projects with progress kits, which often include driver boards, motors, and programming environments. Joining maker communities or local workshops can also provide practical experience and valuable insights into this dynamic field.
—
Feel free to explore this interesting area where efficiency and precision converge seamlessly, paving the way for the innovations of tomorrow!
to sum up
the world of low-voltage DC servo drivers offers a fascinating intersection of efficiency and precision that is reshaping the landscape of automation and control systems. As industries continue to gravitate towards solutions that minimize energy consumption while maximizing performance, these drivers stand at the forefront of innovation. Their ability to provide accurate feedback and smooth operation places them in a unique position to support everything from robotics to aerospace applications.
As we move forward,the ongoing advancements in technology promise to further enhance the capabilities of low-voltage DC servo drivers,ensuring that they remain a pivotal component in our pursuit of more bright,responsive,and sustainable systems. Whether you are an engineer delving into the intricacies of motion control or a business leader seeking to optimize operations, understanding the intricacies of these drivers will undoubtedly prove beneficial.
In this evolving journey, let us continue to explore and embrace the potential of low-voltage DC servo drivers, unlocking new avenues of efficiency and precision that drive the future of technology. Thank you for joining us on this exploration.Your insights and experiences are invaluable as we collectively navigate the exciting horizon ahead.
